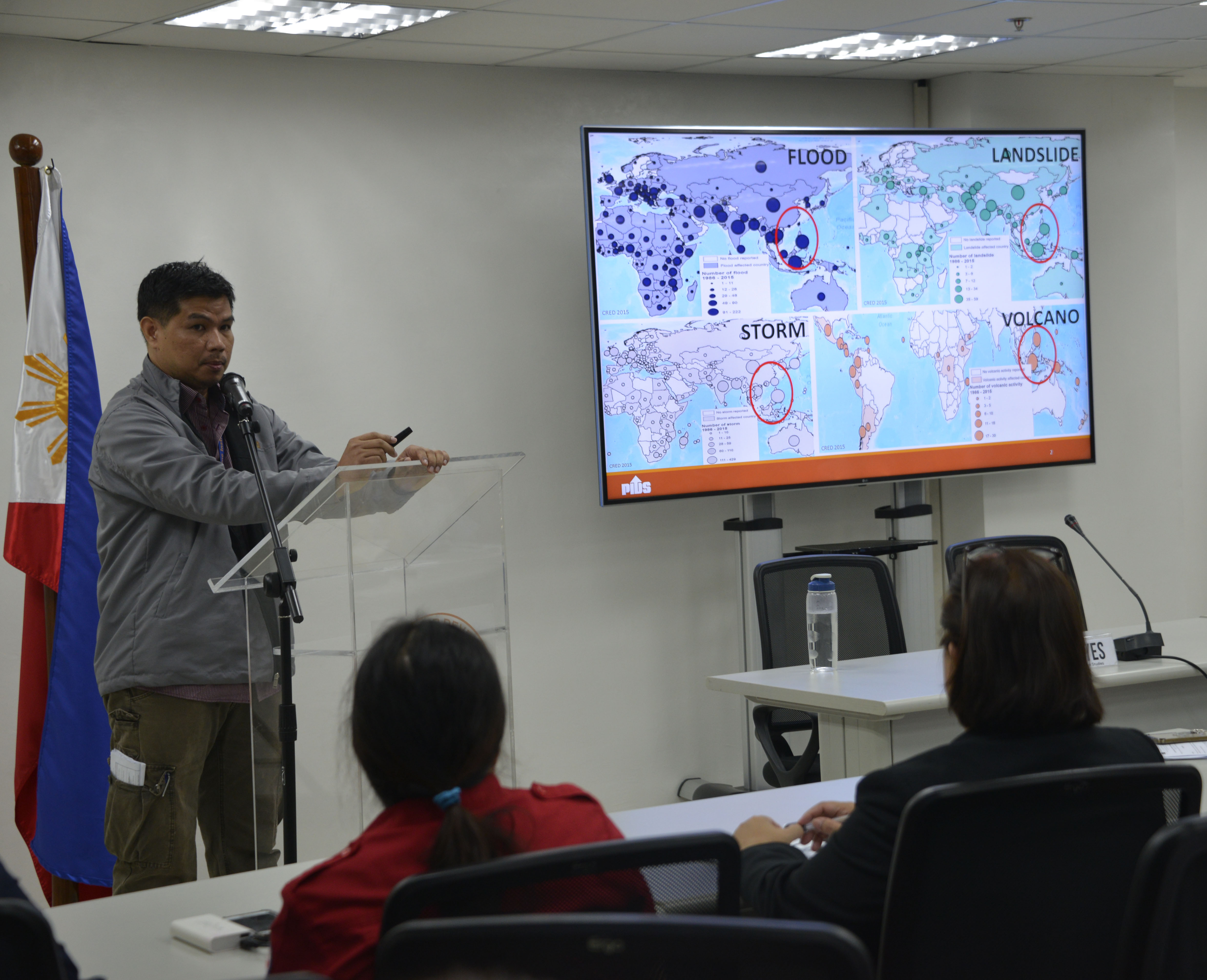
This study examines the grounding and sectoral translation of the National Disaster Risk Reduction Management Plan (NDRRMP), focusing on the thematic areas of disaster prevention and mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery. Republic Act 10121, also known as the Philippine Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Act of 2010, provided for the crafting and implementation of the NDRRMP, outlining the activities aimed at managing risks and strengthening institutional arrangements and capacity at the national and subnational levels. The NDRRMP supposedly outlines the way toward mainstreaming of DRRM and climate change adaptation in policy formulation, development planning, budgeting, and governance with its four priority pillars.
Notwithstanding evident weaknesses in grounding and institutional translation, policy support and departmental creativity exhibited by the theme leaders attest to the competence of local executive servants. It was evident that disaster risk management, as espoused, had influenced development processes and institutional initiatives within five years from the NDRRMP’s launching. Ultimately, strengthening of RA 10121 through appropriate translation and more apt institutional arrangements will ensure the realization of the full potential of the law.
Citations
This publication has been cited 2 times
- Bulan, Amierielle Anne. 2017. Looking beyond rice. Manila Bulletin.
- Celis, Angela. 2017. Unified disaster management body proposed. Malaya Business Insight.