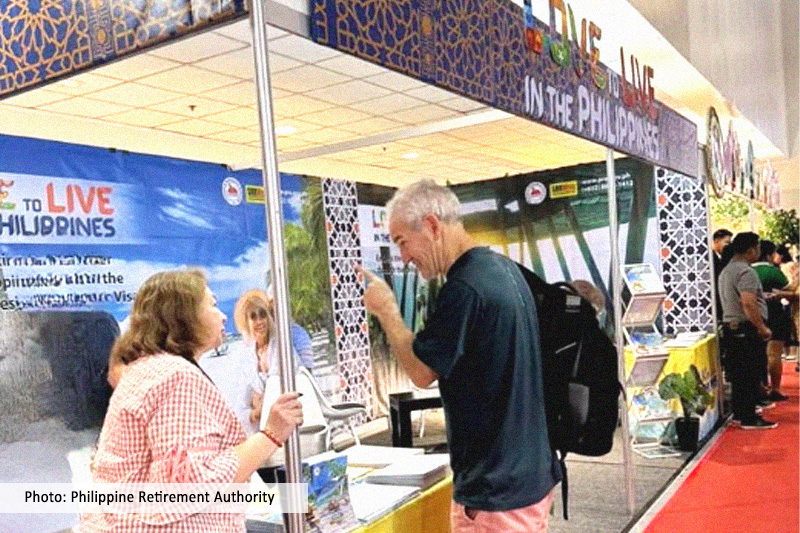
This study assesses the Philippine Retirement Authority's (PRA) current program and business model. Established by Executive Order No. 1037 in 1985, the PRA aims to position the Philippines as a prime retirement destination, contributing to the country's social and economic development. Utilizing GAP and SWOT analyses, the research explores potential enhancements to PRA’s business strategy, guided by Porter's competitive advantage model and Prahalad and Hamel's core competencies framework. In addition, the analysis supplements the analytical frameworks with a strategic agenda that covers a discussion of five strategic dimensions: 1. PRA's goal; 2. PRA’s source of market or competitive advantage; 3. PRA's major source of core competence; 4. PRA's current business model; and 5. PRA's strategies in specific management functions.
The findings reveal PRA's commendable financial performance from 1986 to 2021, achieving fiscal autonomy in 1993. As of December 31, 2021, the agency reported significant financial metrics per retiree. The GAP analysis suggests two pathways for performance improvement: intensifying efforts to meet targets or recalibrating targets to align with available resources, with the SWOT analysis supporting the latter.
Recommendations include enhancing SRRV benefits with a focus on efficient processing and registration, developing a medium-term plan detailing corporate goals and necessary initiatives, promoting a brand identity synonymous with exceptional customer service and the warmth of Philippine hospitality, collaborating with the Department of Tourism to support retirement promotion, and adopting a specialization model to better serve targeted customer segments and regions.
Comments on this paper are welcome within 60 days from the date of posting. Email publications@pids.gov.ph.